Algorithme Gram-Schmidt classique vs modifie
Exercice tire de LN Trefethen & D Bau III, Numerical Linear Algebra, 1997 SIAM Philadelphia
Contents
Precision numerique des algorithmes classique et modifie
on genere deux matrices orthogonales U, V aleatoirement
[U,X] = qr(rand(80)); [V,X] = qr(rand(80)); % matrice diagonale avec elements exponentiellement decroissants S = diag(2.^(-1:-1:-80)); % matrice avec valeurs propres lambda = diag(S) A = U*S*V; % on calcule les factorisations QR classique et modifie [QC,RC] = clgs(A); [QM,RM] = mgs(A); % on trace les elements diagonaux de R semilogy(1:80,diag(RC),'x',1:80,diag(RM),'o') % on ajoute les lignes correspondant a epsilon machine et sa racine carree hold on plot(1:80,(1:80)*0 + sqrt(eps),'--',1:80,(1:80)*0 + eps,'-.')
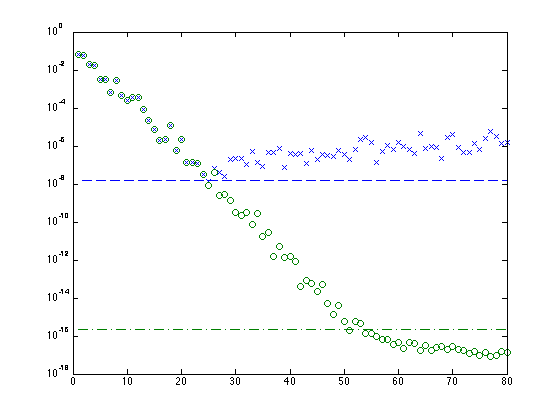
Perte d'orthogonalite
A = [0.70000 0.70711;
0.70001 0.70711];
% on calcule QR avec matlab (Householder)
[Q,R] = qr(A);
% on teste l'othogonalite
norm(Q'*Q-eye(2)) % = 0 pour matrice orthogonale
% on calcule QR avec MGS
[Q,R] = mgs(A);
% on teste l'othogonalite
norm(Q'*Q-eye(2)) % = 0 pour matrice orthogonale
ans = 2.3515e-16 ans = 2.3014e-11
On perd 5 decimales de precision par rapport a l'algo de Matlab
Codes
type mgs type clgs
function [Q,R] = mgs(A)
% MGS modified Gram-Schmidt algorithm
%
% See also CLGS, QR
%
% tire de: LN Trefethen & D Bau III, Numerical Linear Algebra, 1997 SIAM Philadelphia
[m,n] = size(A);
v = A;
R = zeros(n,n);
Q = zeros(m,n);
for i=1:n
v(:,i) = A(:,i);
end
for i=1:n
R(i,i) = norm(v(:,i),2);
Q(:,i) = v(:,i)/R(i,i);
for j = (i+1):n
R(i,j) = (conj(Q(:,i))')*v(:,j);
v(:,j) = v(:,j) - R(i,j)*Q(:,i);
end
end
function [Q,R] = clgs(A)
% CLGS classical Gram-Schmidt (unstable)
%
% See also MGS, QR
%
% tire de: LN Trefethen & D Bau III, Numerical Linear Algebra, 1997 SIAM Philadelphia
[m,n] = size(A);
v = zeros(m,n);
R = zeros(n,n);
Q = zeros(m,n);
for j=1:n
v(:,j) = A(:,j);
for i=1:j-1
R(i,j) = (conj(Q(:,i))')*A(:,j);
v(:,j) = v(:,j) - R(i,j)*Q(:,i);
end
R(j,j) = norm(v(:,j),2);
Q(:,j) = v(:,j)/R(j,j);
end