The Wagner Projections (Part 2)
Usage
Note: I’m no cartographer. The recommendations below are made by a complete layman!
Wagner’s family of nine projections with
reasonably chosen characteristics is of course offering a wide range of
possible applications.
I’m inclined to say that for usual world maps – i.e.
like those you see in atlases and lexica, on news programs and
newspaper articles, on wallpaper maps etc. –, you can
modify an old idiom that is used amongst typographers:
When in doubt, use Wagner.
[1]
Of course, I’m not saying that Wagner’s always the best possible choice but, as a rule, using Wagner you’re never completely wrong. (Except for special cases like navigation where you still will refer to Mercator, or radio work which normally uses the azimuthal equidistant projection for good reasons.)
Having said that, the question remains which one of the nine Wagner projections should be used for a certain application. I’d like to show my own answers to this very question.
Topographic Map
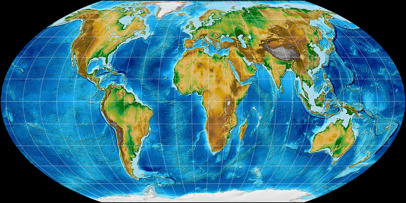
Wagner IV projection, topographic
![]() ToJu
ToJu
As I’ve said before: For a topographic map,
I’d always choose an equal-area projection – so in this case, that
leaves Wagner I, IV and VII. I’ll discard Wagner I first, since
sinusoidal meridians are very uncommon nowadays.
Out of the remaining two projections, I prefer Wagner VII:
Africa is elongated a little bit less and it has better distortion values in the corners.
Nonetheless, Wagner IV still seems to be a good choice in case you prefer straight parallels.
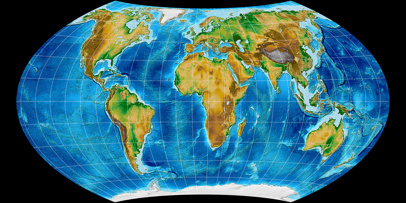
Wagner VII projection, topographic ![]() ToJu
ToJu
So that was the easy part.
For the other kinds of maps, it was much harder for me to come to an decision. Not because I didn’t find
a decent variant but because I had too many projections that’ll serve…
Political Map
Before we look at examples of political maps
using Wagner projections, I’d like to digress a bit by asking:
Does a political map have to be equal-area?
The short answer is: No, I don’t think so.
Arno Peters, in contrast, thought that an equivalent map
is mandatory in terms of equality and justice.
No country is favored, no country is disadvantaged. But
will the size of a country tell you anything about its significance or
about its power?
I think history taught otherwise. What is a significant country anyway? In many regards, the most significant country in the world
is the one you happen to live in.
Moreover, does an equal-area map really
help you to evaluate countries’ sizes?
Of course, an equivalent map will not make you think
that Greenland is bigger than South America (as does the Mercator
projection) when actually,
South America is about seven times larger.
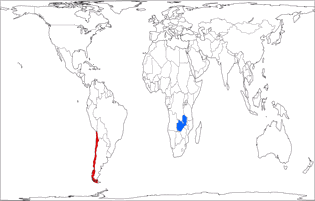
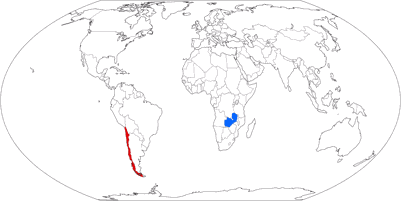
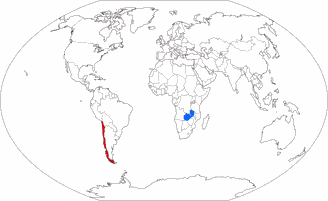
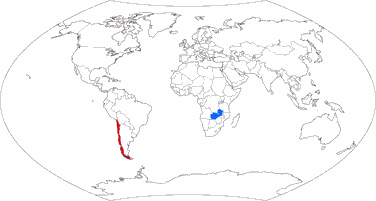
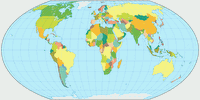
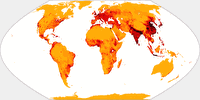
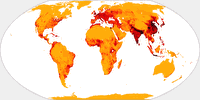
But look at these images where I’ve highlighted Chile
(red) and Zambia (blue). These two countries have virtually the same
size. [2]
Can you tell it just by the look of it? I surely can’t. I
can see that they are, well, roughly in the same ballpark. But you can
see that
even on projections that definitely aren’t equal-area,
e.g. the well-known Winkel Tripel or Wagner’s approximation towards
Winkel, Wagner IX.
On that account, I don’t think that you need an
equal-area projection for a political map.
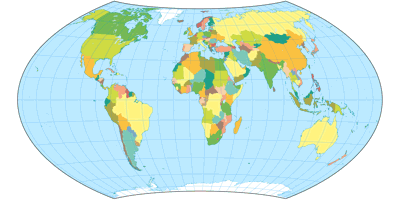
Wagner VII projection, political ![]() ToJu
ToJu
Having said that, let’s move on to my actual recommendations.
Firstly, there's the the equivalent Wagner VII…
Huh? Didn’t I just tell you that a political map doesn’t have to be equal-area?
Of course, I did, but I didn’t say that a political map may never be equal-area. And in my opinion,
Wagner VII is one of the best equal-area projections there is – at least, among the pole line projections.
So if you want an equal-area political map, Wagner VII is a very good pick – but I’d also take Strebe 1995 into consideration.
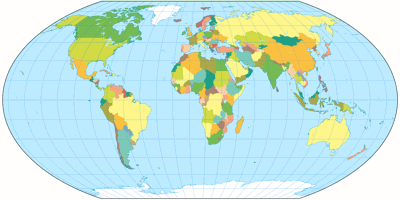
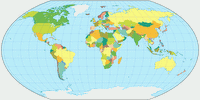
Wagner V projection, political ![]() ToJu
ToJu
If you prefer straight parallels, I recommend Wagner V, an aphylactic
projection which has better shapes than its equal-area counterparts but still
is quite close to equivalence, so you get a good idea of the size relationships.
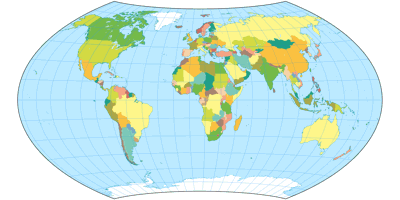
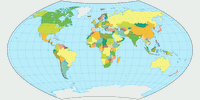
Wagner VIII projection, political ![]() ToJu
ToJu
But my favorite in this area is Wagner VIII: It offers the compromising properties of the Wagner V but with curved parallels (like Wagner VII) to furtherly enhance the shapes.
Karl-Heinz Wagner himself seemed to think
likewise, because in the german Columbus atlas of 1961, which was edited
by Wagner,
he chose Wagner VIII for the world map.
Who am I to disagree? ;-)
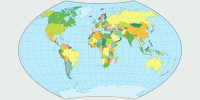
But remember these are only my favorites. Basically I think that you can use any of the Wagner projections for a political map, therefore I’ll add images of the other ones, too. See for yourself.
Climatic Map
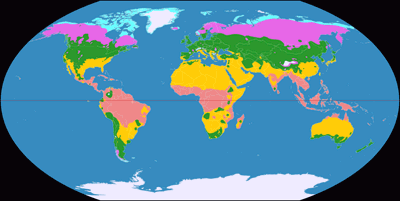
Wagner VI, Climatic Map ![]() ToJu
ToJu
I’ve said it before:
The climate zones are related to the latitudes: As a rule of thumb, you can say that it gets colder
the farther you move away from the equator.
And that’s the reason why I’d always recommend a
projection with straight parallels for a climatic map.
And moreover, I’d prefer equally spaced parallels. Of
course, this exaggerates the total size of the polar zones,
but keeps their real north-to-south extension which is
more important in this case (at least, in my opinion).
That leaves us with Wagner III and VI.
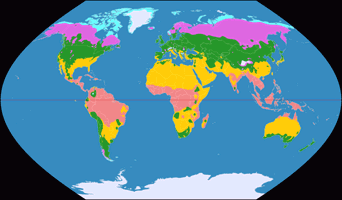
Wagner III (40°), Climatic Map ![]() ToJu
ToJu
Considering the fact that meridians using elliptic curves are much more common nowadays, most people would probably choose Wagner VI, nonetheless I do think that Wagner III with its sinusoidal meridians does make a fine climatic map, especially if you use the option to set the standard parallel arbitrarily.
If you decide to set the standard parallel at e.g. 40° North/South, you’ll end up with an image that uses less horizontal space without loosing any information – and which has, according to Wagner himself, »a better distribution of distortion«. Even if you don’t agree with that… well, honestly I don’t think that distortions of shape have to be avoided at all costs in a climatic map.
Thematic Maps
For a thematic map it’s of course crucial which kind of information you want to display. Wagner’s well developed family of projections includes good options for about any purpose – but let’s start the other way round by showing a thematic map where a Wagner projection might not be the best choice: For a climatic map, I recommended a projection with straight parallels since the phenomenon that is displayed is closely related to the latitude. Consequently, I have to recommend a projection with straight meridians (i.e. a cylindric projection) when the phenomenon is closely related to the longitude. But there is no cylindric projection among Wagner’s projections.
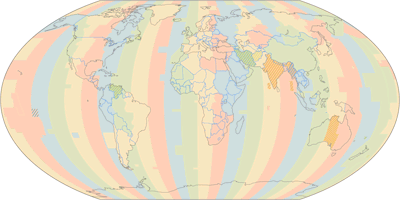
Wagner V, time zones ![]() ToJu
ToJu
On the other hand, I don’t think that a time zone map using a pseudocylindrical projection is incomprehensible, and on the upside, it even gives you the (right!) idea that the time zones converge towards the poles. Since I don’t see any point in preserving the shapes of the continents or proportions of size here, my pick is the aphylactic Wagner V.
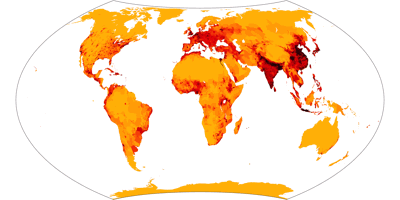
Wagner VII, population density ![]() ToJu
ToJu
The next choice is quite easy:
Whenever densities of phenomena are to be shown, of course an equal-area map is best. So again, the choice is
between Wagner I, IV and VII; and again Wagner VII is my favorite.
However, this is mostly an aesthetic choice, so let’s at least take a look at the same map using Wagner I and IV:
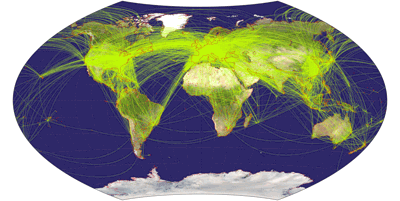
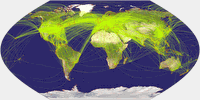
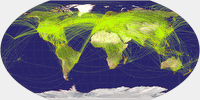
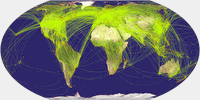
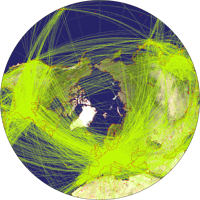
Wagner IX, airline traffic ![]() ToJu
ToJu
Now, this one is a fine example that you
have to choose wisely when preparing a thematic map: When showing the
airline traffic
around the world you have to consider that a lot of
traffic passes the north polar areas. So it’s a good idea to favor
a projection that doesn’t vertically compress this area,
otherwise the map might become confusing.
So that’s a call for Wagner’s projections with equally spaced parallels.
Being a fan of the lenticulars, my favorite is Wagner IX, but III and VI will do nicely, too.
Here are the latter projections, accompanied by Wagner IV which, being an equal-area projection, compresses in north-south direction and therefore serves as a bad example.
By the way, the air line traffic maps might be a good example to teach students that sometimes, map projections can fool you if you don’t know how to read them: On these maps it seems that the planes take a turn north of Canada and Siberia. Of course, they don’t. They follow a straight line as you can clearly see on the azimuthal equidistant projection.
Note: I dropped the Early human migrations map that I used in the articles about Patterson and Strebe. It was an ill-chosen example in the first place, since a map like this will work with most projections.
Decorative Element
On the decorative renderings of the Wagner projections I didn’t get the results I was expecting: Before I was actually generating them, I expected the pseudocylindricals with elliptical meridians (i.e. Wagner IV, V, VI) to look best by far. I thought that the pronounced shearing of the sinusoidal pseudocylindricals (Wagner I, II, II) as well as the curved parallels and pole lines of the lenticular projections (Wagner VII, VIII, IX) would make them… well, look wrong when stripped of their graticules and outer borders.
But when I examined the finished maps, I came to different conclusions.
- On the equal-area variants (Wagner I, IV and VII) the polar regions and especially Greenland were too squished for my taste;
- whereas on the projections with equally spaced parallels (III, VI, IX) Greenland’s enlargement attracted negative attention far more than if you use the very same projections on other maps (such as political);
- the shearing and the curved parallels mentioned above didn’t stand out as much as I expected.
So the bottom line so far is that the compromise projections Wagner II, V and VIII are the ones that I like best. And among those, Wagner V is my favorite – the pseudocylindric projection with elliptic curves. So after all, something turned out as I expected. However, there was another surprise: I liked the modified Wagner IX which is called IX.i here just as much as Wagner V.
So in this case, I’m showing all of the ten variants. See what works best for you:
Conclusion
As I’ve said in the beginning, you’ll find
an appropriate Wagner projection for a lot of purposes. I hope I was
able to show that.
Of course there are always alternatives that might work
just as well or sometimes, even better:
For pseudocylindric equal-area maps, there’s always
Eckert’s work, and the Hufnagel projections will give you a great amount of
freedom in design; for equivalent lenticular maps check out Strebe 1995 and 2011.
If you prefer a compromise map, the popular Robinson and
Winkel Tripel projections are a safe choice, but also consider the
Canters or Ginzburg projections.
And so on and so forth.
But if you need a bunch of projections with different properties, that (for the sake of homogeneity) still have a similar appearance, the Wagner family of projections is an excellent choice.
And with Wagner I through IX you still haven’t reached end of the possibilities that the Wagner transformation method (»Umbeziffern«) offer. I’m going to elaborate on that in the third part of the series of articles.
Footnotes
-
↑
The typographic idiom is: When in doubt, use Caslon.
Caslon is a 18th century typeface that is known for its legibility. -
↑
Land area of Chile: 743,812 km² / 287,187 sq mi
Land area of Zambia: 743,398 km² / 287,028 sq mi
Total area of Chile: 756,102 km² / 291,933 sq mi
Total area of Zambia: 752,612 km² / 290,585 sq mi
[Source of data]
Back to Selected Projections • The Wagner Projections (Part 1) • Part 3: Umbeziffern • Go to top